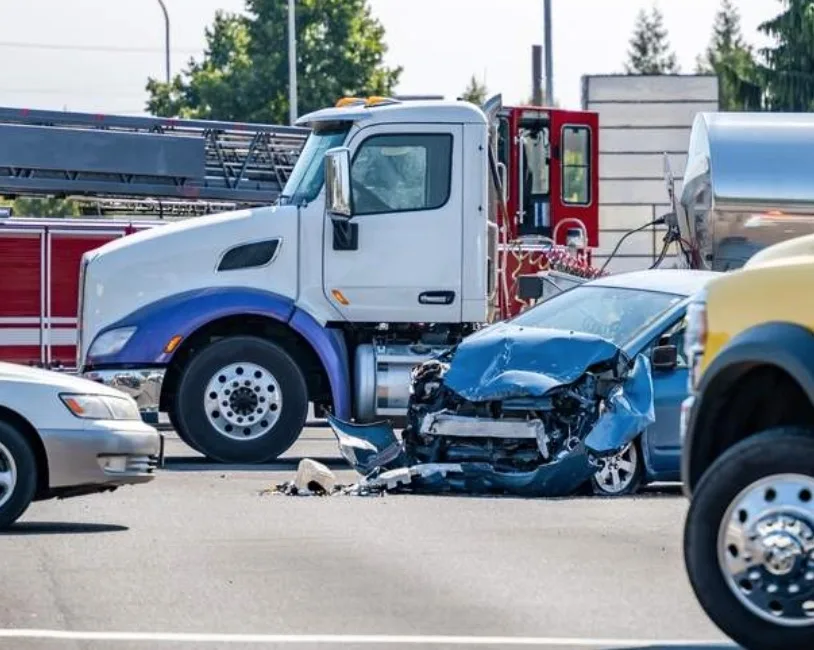
Blunt force head trauma occurs when a forceful object strikes the skull or brain without penetration. This type of injury can result from car accidents, falls, physical assaults, or workplace accidents. Depending on the intensity of impact and location, blunt force trauma may cause minor concussions or lead to life-threatening brain damage.
The brain can collide with the inside of the skull, causing bleeding, bruising, or swelling, known as a traumatic brain injury (TBI). If you suffered a brain injury from an accident in Houston that was not your fault, contact an attorney right away for legal help.
Common Causes of Blunt Force Head Injuries
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car, truck, motorcycle, and pedestrian accidents are among the most frequent causes of blunt head trauma. High-speed collisions often cause occupants to strike their heads on the steering wheel, windows, dashboard, or the ground. Even with airbags and seatbelts, the impact can cause skull fractures, hematomas, or severe concussions.
Falls and Slip-and-Fall Accidents
Falls from ladders, stairs, scaffolding, or slippery surfaces can result in a head injury. Elderly individuals are especially at risk, and these incidents often occur in nursing homes or poorly maintained properties.
Workplace and Construction Site Accidents
Head trauma is common in industrial and construction environments. Falling tools, debris, or heavy machinery may strike workers. Failure to use proper protective headgear, such as hard hats, increases the risk of serious injuries.
Sports-Related Injuries
Athletes in contact sports like football, boxing, or hockey face high risks of blunt trauma. Repeated hits to the head can cause long-term neurological damage, including chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
Types of Blunt Force Head Injuries
Concussions
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury caused by sudden movement of the brain inside the skull. Symptoms include dizziness, headache, nausea, confusion, and short-term memory loss. Although labeled “mild,” concussions can lead to post-concussion syndrome or second-impact syndrome if not treated properly.
Contusions and Brain Bruising
A brain contusion refers to localized bleeding or bruising within the brain tissue. It is usually caused by direct impact and can lead to swelling, increased intracranial pressure, and neurological deficits.
Skull Fractures
A skull fracture occurs when the bones of the skull break due to a powerful impact. Types include linear, depressed, diastatic, and basilar fractures. Basilar skull fractures—located at the base of the skull—can be particularly dangerous, potentially damaging cranial nerves or causing cerebrospinal fluid leaks.
Intracranial Hemorrhage
This refers to bleeding inside the skull and includes subdural hematomas, epidural hematomas, and intracerebral hemorrhages. Hemorrhages can compress brain tissue, leading to permanent impairment or death without emergency treatment.
Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)
This severe brain injury occurs when the brain rapidly shifts inside the skull, tearing axons (nerve fibers) in the process. DAI often results in coma or long-term cognitive disability and is commonly seen in high-impact crashes.
Blunt Force Trauma to the Head- Symptoms to Watch Out For
Signs of head trauma vary based on severity but may include:
• Loss of consciousness
• Persistent headache
• Nausea and vomiting
• Memory loss or confusion
• Blurred vision
• Slurred speech
• Seizures
• Unequal pupil size
• Fluid drainage from the nose or ears
• Difficulty waking or being extremely tired
Always seek medical attention after a blow to the head.
Long-Term Effects of Blunt Force Head Trauma
Victims may face long-term or permanent consequences such as:
• Cognitive impairment
• Memory loss
• Emotional or behavioral changes
• Speech and language difficulties
• Chronic headaches or migraines
• Seizure disorders
• Loss of motor skills or coordination
• Coma or vegetative state
• Reduced quality of life
• Loss of earning capacity
Recovery after an accident will vary depending on the severity of the injury.
Diagnosis of Brain Injuries
Tools such as CT scans and MRIs are used to evaluate brain damage. Also, neurological exams focus on cognitive function.
Treatment Options for Head Trauma
Treatment may include:
• Hospital observation and monitoring
• Surgical intervention to relieve pressure or remove blood clots
• Medication to reduce swelling and control seizures
• Physical, occupational, and speech therapy
• Cognitive rehabilitation for memory and attention restoration
• Psychological counseling for trauma-related mental health issues
Severe cases may require long-term residential care or assisted living arrangements.
Legal Rights After Blunt Force Head Trauma
When blunt force head trauma results from another party’s negligence, victims have the right to pursue a personal injury claim. Common legal grounds include:
• Car accidents caused by reckless drivers
• Premises liability for unsafe conditions
• Defective products or a lack of proper safety equipment
• Construction site or industrial negligence
• Workplace accidents
Proving Liability in Head Trauma Cases
To recover damages, claimants must prove negligence, which is:
• The defendant owed a legal duty of care
• That duty was breached through negligence or wrongdoing
• The breach directly caused the blunt force trauma
• The victim suffered actual harm and losses
Evidence may include accident reports, witness testimony, surveillance footage, medical records, and expert opinions.
Compensation for Victims of Blunt Force Head Trauma
Injury victims may be entitled to recover:
• Medical expenses (past and future)
• Lost wages and diminished earning capacity
• Pain and suffering
• Mental anguish and emotional distress
• Loss of enjoyment of life
• Long-term care
Given the seriousness of a traumatic brain injury, the potential for a large settlement or jury verdict goes up substantially.
Why Get an Attorney Right Away
One of the key points to a successful personal injury claim is the documentation and proof of your injury. Hiring an expert brain injury attorney can help ensure that your injury is properly documented for maximum impact.
Contact the Houston personal injury law firm of Baumgartner Law Firm at (281) 587-1111.
Baumgartner Law Firm
6711 Cypress Creek Pkwy
Houston, TX, 77069